Blog
How to Detect and Prevent Deepfake Attacks in Cybersecurity

How to Detect and Prevent Deepfake Attacks in Cybersecurity
The rise of deepfake attacks in cybersecurity has become a significant concern for individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. As AI-generated cyber threats evolve, cybercriminals exploit deepfake technology for fraud, misinformation, and identity theft.
With the ability to manipulate video, audio, and text, deepfakes create serious cybersecurity risks that impact financial institutions, corporate security, and even national security. A study found that deepfake videos online doubled in just nine months, reaching over 15,000 by the end of 2019. The numbers have surged since then, making deepfake scams in business a critical issue.
Organizations must take proactive measures to detect and prevent deepfake-related fraud. This article explores how to detect deepfake attacks, examines deepfake detection techniques, and discusses strategies for preventing deepfake scams before they cause irreversible damage.
What Are Deepfakes?
Deepfakes are artificial media created using deep learning algorithms, primarily leveraging Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). GANs function by having two neural networks—the generator and the discriminator—compete against each other. The generator produces fake content, while the discriminator tries to detect whether the content is real or fake. Over time, the generator improves its ability to create hyper-realistic images, voices, and videos that can be nearly impossible to distinguish from authentic content.
Originally developed for entertainment purposes, such as dubbing actors’ performances or de-aging characters in movies, deepfake technology has now become a serious cybersecurity risk. Criminals and malicious actors exploit deepfakes to commit fraud, manipulate public opinion, and engage in cyber espionage.

Types of Deepfakes
Three primary forms of deepfake technology pose cybersecurity threats:
1. Video Deepfakes
Video deepfakes involve the alteration of a person’s face and expressions to create the illusion that they said or did something they never actually did. Some examples include:
- A CEO appearing to approve a financial transaction in a fraudulent video.
- A politician seemingly making controversial statements, fueling misinformation campaigns.
- An employee’s face being superimposed onto another person’s body to gain access to security systems that rely on facial recognition.
A famous example is the deepfake video of former U.S. President Barack Obama, where an AI-generated version of his voice and face was used to say things he never actually said. Such realistic fabrications highlight the dangers posed by this technology.
2. Audio Deepfakes
Deepfake phishing scams increasingly rely on AI-generated voice cloning to impersonate individuals. Attackers use this method to
- Call an employee and convince them to transfer money or disclose sensitive information.
- Leave fake voicemails pretending to be a bank representative or an executive.
- Conduct social engineering attacks by impersonating loved ones or colleagues.
3. Text-Based Deepfakes
AI-generated text can be used to create misinformation, phishing emails, and fraudulent messages. With the rise of AI language models, attackers can generate convincing emails that
- Mimic an executive’s writing style and request sensitive information.
- Fabricate entire news articles that spread political or financial misinformation.
- Generate fraudulent documents for identity theft or financial fraud.
- A real-world example of text-based deepfakes includes AI-generated phishing emails designed to trick employees into sharing passwords or sending money.
The Cybersecurity Risks of Deepfake Attacks
1. Business Email Compromise (BEC) & Fraud
One of the most alarming uses of deepfake technology is in Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams, where attackers use deepfake audio and video to impersonate high-ranking executives or company officials. Fraudsters manipulate employees into transferring large sums of money or sharing sensitive information, believing they are following legitimate orders.
How It Works:
- Attackers gather publicly available video and audio clips of a target (e.g., CEOs, managers).
- Using AI-generated cyber threats, they clone the person’s voice or face.
- A manipulated video call or phone call is made to employees requesting urgent financial transactions.
- Since the deepfake is highly realistic, employees comply, leading to substantial financial losses.
Implications:
- Increased risk of financial fraud within organizations.
- Loss of trust in remote communication methods such as emails and phone calls.
- Need for advanced deepfake fraud prevention strategies in corporate environments.
2. Disinformation Campaigns
Deepfakes are also widely used to spread misinformation, especially on social media. Malicious actors, including political groups and foreign adversaries, use deepfake scams in business and politics to damage reputations, manipulate public opinion, and fuel social unrest.
Why This Is Dangerous:
- Hard to control once misinformation spreads online.
- Damages corporate reputations and political stability.
- Affects financial markets and investor confidence.
How to Combat Deepfake Disinformation:
- Social media platforms must implement AI-powered deepfake detection.
- Governments need strict legal actions against AI-generated cyber threats.
- Businesses should monitor for deepfake scams in business and preemptively counter misinformation.
3. Identity Theft & Social Engineering
Deepfakes have become a powerful tool for identity theft. Criminals use them to bypass security measures such as facial recognition and voice authentication, making deepfake identity theft prevention a growing concern.
How Deepfakes Are Used for Identity Theft:
- Attackers create deepfake videos of individuals to deceive facial recognition-based security systems.
- They use audio deepfakes to trick financial institutions into granting access to personal accounts.
- They manipulate customer service call centers by mimicking a victim’s voice.
Implications:
- Traditional identity verification methods have become unreliable.
- Financial and corporate security systems must evolve to counter AI-driven fraud.
- Deepfake identity theft prevention requires multi-factor authentication beyond voice or facial recognition.
Preventative Measures:
- Companies should use liveness detection in biometric security.
- Employees must be trained to recognize deepfake phishing scams.
- Banks should require multi-step verification for large transactions.
4. Cyber Espionage & Nation-State Attacks
Governments and intelligence agencies are increasingly targeted by AI-generated cyber threats, making deepfake attacks in cybersecurity a national security issue. Foreign adversaries and cybercriminal groups use deepfakes to conduct espionage, manipulate elections, and extract sensitive information.
How Deepfake Espionage Works:
- Impersonating Government Officials: Attackers use deepfake video or audio deepfakes to impersonate diplomats or defense personnel.
- Disrupting Elections: Deepfakes of political candidates making false statements can alter election results.
- Corporate Espionage: Rival companies use deepfakes to infiltrate organizations and gain trade secrets.
Consequences:
- National security risks due to misinformation campaigns.
- Economic impact from corporate espionage and intellectual property theft.
- Increased difficulty in verifying authentic communications in sensitive sectors.
Countermeasures:
- Government agencies must deploy AI-powered deepfake detection tools.
- Strict cybersecurity policies should be in place to verify official communications.
- Increased collaboration between cybersecurity firms and intelligence organizations to track AI-generated cyber threats.
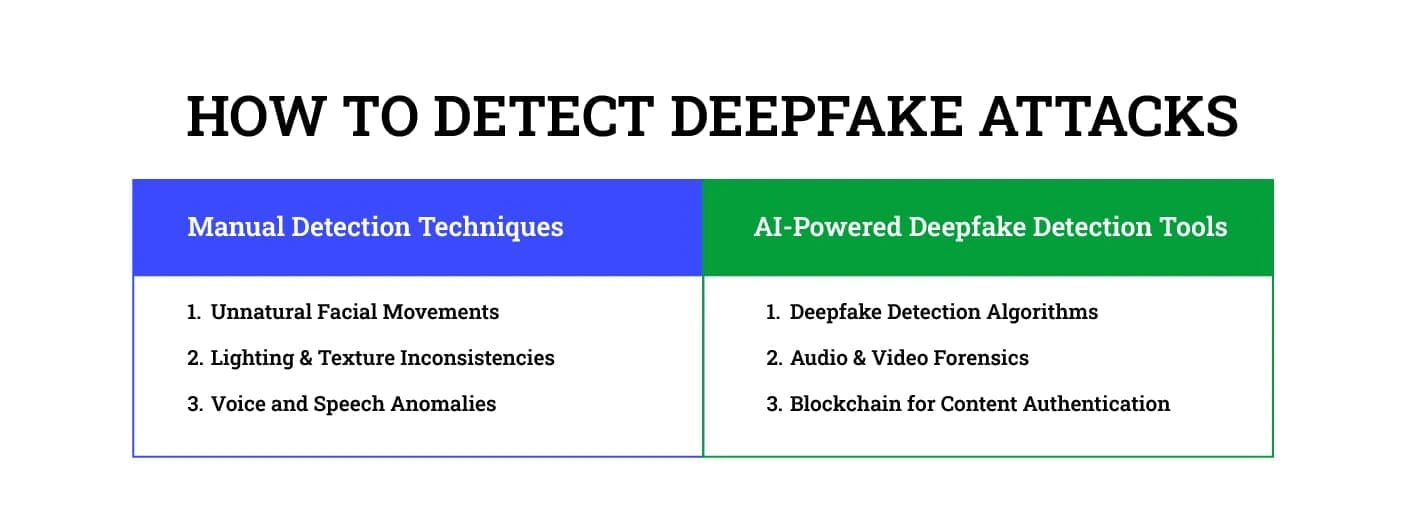
How to Detect Deepfake Attacks
With deepfakes becoming increasingly realistic, detection requires both human observation and advanced AI-driven tools. Recognizing deepfakes can be challenging, but a combination of manual detection techniques and AI-powered deepfake detection methods helps in identifying these cyber threats.
A. Manual Detection Techniques
While AI-generated deepfakes are becoming more sophisticated, some subtle flaws can still reveal their fabricated nature. Careful human analysis can expose these inconsistencies:
- Unnatural Facial Movements:
- Irregular Blinking: Many deepfake videos struggle with accurate eye blinking, either causing a person to blink too frequently or not at all.
- Awkward Lip-Syncing: The synchronization between speech and lip movements often appears slightly misaligned, leading to unnatural-looking speech.
- Distortions Around the Mouth: When a person speaks, the area around the lips may flicker or warp, indicating AI manipulation.
- Lighting & Texture Inconsistencies:
- Shadows & Reflections: Deepfakes may exhibit lighting inconsistencies, where shadows don’t align with the environment or reflections appear distorted.
- Skin Texture Issues: AI-generated faces sometimes lack the natural imperfections of human skin, appearing overly smooth or inconsistent in texture.
- Blurred or Warped Areas: Certain regions of a deepfake image, such as the edges of the face, ears, or hairline, may look blurry or have unnatural distortions.
- Voice and Speech Anomalies:
- Robotic or Synthetic Tones: Even though AI voice cloning is improving, some deepfake voices still sound artificial, with subtle glitches in tone, pitch, or emotion.
- Odd Pronunciation & Accents: Mispronounced words, inconsistent accents, or unnatural pauses in speech patterns can indicate a deepfake-generated voice.
- Mismatched Voice Modulation: Human speech naturally includes small variations in pitch and volume, whereas AI-generated voices may sound too smooth and monotone.
B. AI-Powered Deepfake Detection Tools
Since manual detection has limitations, AI-powered deepfake detection is essential for identifying and mitigating AI-generated cyber threats. The following tools and techniques help in detecting deepfakes more accurately:
- Deepfake Detection Algorithms:
- AI models trained on vast datasets can analyze videos and detect manipulation techniques used in GAN-generated deepfakes.
- These models examine facial expressions, head movements, and blinking patterns to distinguish real vs. fake content.
- Audio & Video Forensics:
- AI forensic tools scan for anomalies in voice, background noise, and speech inconsistencies.
- Frame-by-frame analysis of videos can detect glitches or inconsistencies that indicate deepfake phishing scams.
- Blockchain for Content Authentication:
- Blockchain technology is being explored as a way to verify the authenticity of video and image content.
- By recording original content on a blockchain ledger, businesses can validate whether media has been altered, reducing the risk of deepfake scams in business.
Preventing Deepfake Attacks in Cybersecurity
Prevention is key to mitigating the dangers posed by deepfake attacks in cybersecurity. Organizations need to implement multi-layered security strategies to identify, block, and prevent deepfake cyber fraud before it causes damage.
A. Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) & Biometric Security
Deepfakes can effectively mimic voices and faces, making traditional biometric security vulnerable. To counter this, organizations should implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and advanced biometric verification techniques:
- Liveness Detection in Biometric Security:
- Unlike traditional facial recognition, liveness detection requires users to perform random actions like smiling or blinking to verify their presence.
- This prevents attackers from using deepfake videos to bypass security measures.
- Beyond Voice Authentication:
- Since voice deepfake cybersecurity risks are increasing, businesses should avoid relying solely on voice-based authentication.
- Instead, combining voice verification with PINs, passwords, or one-time passcodes (OTP) enhances security.
B. Strengthening Email & Communication Security
To protect against deepfake phishing scams, businesses must secure internal communications and educate employees on recognizing AI-generated threats:
- AI-Driven Email Security Solutions:
- AI-powered tools can scan emails for AI-generated cyber threats, flagging suspicious or manipulated content.
- These tools analyze writing patterns, metadata, and sender authentication to detect deepfake-generated phishing emails.
- Employee Awareness & Training:
- Employees should be trained to recognize deepfake-related scams, such as fraudulent video calls or voice commands from fake executives.
- Regular phishing awareness programs should include deepfake detection techniques to prevent deepfake scams in business.
- Strict Verification Protocols for Financial Transactions:
- Companies should implement strict verification procedures, such as requiring a secondary confirmation via a secure channel before processing high-value transactions.
- Using encrypted communication channels ensures that cybercriminals cannot intercept sensitive information.
C. AI-Driven Fraud Prevention & Threat Intelligence
AI-powered security systems can proactively detect fraudulent activities associated with deepfake attacks. Businesses should incorporate AI-driven fraud prevention into their cybersecurity strategies:
- Real-Time AI-Powered Fraud Detection:
- AI algorithms analyze transaction patterns to identify suspicious behavior, such as unusual payment requests or login attempts from unfamiliar locations.
- These fraud detection systems help reduce the risk of deepfake identity theft prevention failures.
- Deepfake Monitoring for Executive Communications:
- Companies should monitor high-risk communications, such as executive emails and video conferences, for signs of deepfake manipulation.
- AI tools can compare real-time video feeds with stored biometric data to verify authenticity.
- Threat Intelligence to Detect AI-Generated Cyber Threats:
- Cybersecurity teams should leverage real-time threat intelligence to stay updated on emerging deepfake scams and tactics used by attackers.
- By integrating deepfake detection into cyber threat intelligence platforms, businesses can proactively defend against attacks.
D. Regulatory & Legal Frameworks Against Deepfakes
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are enacting laws and guidelines to combat deepfake attacks in cybersecurity. Organizations should comply with these regulations to strengthen deepfake fraud prevention efforts:
- US National Defense Authorization Act:
- This law mandates research on deepfake detection techniques to address national security threats posed by AI-generated deepfakes.
- EU’s AI Act:
- The European Union has introduced the AI Act, which aims to regulate high-risk AI applications, including AI-generated cyber threats used in fraud and misinformation.
- Corporate Compliance & Ethical AI Use:
- Businesses should follow ethical AI guidelines, ensuring their AI tools are not misused to create or distribute deepfakes.
- Compliance with cybersecurity regulations helps organizations establish deepfake identity theft prevention measures.
How Paramount Helps Businesses Defend Against Deepfake-Related Cyber Threats
Paramount provides cutting-edge cybersecurity solutions to protect businesses from deepfake attacks in cybersecurity. Our services include:
- AI-powered deepfake detection tools to monitor and flag suspicious media.
- Deepfake fraud prevention strategies tailored to organizational needs.
- Cybersecurity risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and strengthen defenses.
By partnering with Paramount, companies can take proactive steps in preventing deepfake scams and safeguarding critical assets.
Conclusion
The threat of deepfake attacks in cybersecurity is growing rapidly, with fraudsters leveraging AI to manipulate video, audio, and text. Businesses and governments must adopt deepfake detection techniques and strengthen cybersecurity measures to combat AI-generated cyber threats.
From deepfake phishing scams to identity theft prevention, organizations must stay ahead of attackers by integrating AI-powered deepfake detection and fraud prevention tools. By implementing robust security frameworks and regulatory compliance, companies can effectively mitigate the risks posed by deepfakes.
For expert guidance on how to prevent deepfake cyber fraud, contact Paramount today and safeguard your business from the evolving cyber threats of tomorrow.
Recent Posts

Protect your online assets from cyber threats with Paramount

Comprehensive cyber security solutions for individuals and businesses

Significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats and ensure a safer digital environment.
