Blog
Preparing for Data Privacy Compliance: A Guidee

Preparing for Data Privacy Compliance: A Guide
Data privacy is a growing concern for businesses today. With stricter regulations in place, companies need to protect personal information and gain consumer trust. This guide covers key data privacy rules in the GCC, how AI can help with compliance and practical tips for building a strong privacy program. Whether you’re just getting started or improving your approach, this blog will help you navigate the path to data privacy compliance.
Addressing Data Privacy Concerns in Modern Business
Data privacy has become a cornerstone of trust between organizations and their consumers. As businesses increasingly rely on digital technologies to store and process data, the risks of breaches and misuse grow. In fact, 93% of organizations rank privacy among their top 10 business risks , with 36% placing it in the top five. This highlights the critical need for robust privacy compliance strategies to safeguard both corporate reputation and consumer trust.
For businesses in the GCC region, data privacy compliance isn’t just a legal mandate; it’s an essential part of corporate governance and risk management. With emerging trends such as AI integration and automation shaping the future of privacy, businesses must remain agile and proactive in their approach.
Overview of Key Privacy Regulations in the GCC Region
The GCC region has witnessed a surge in regulatory frameworks aimed at protecting personal data. Some of the notable regulations include:
-
Saudi Arabia’s Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL):
This law, effective September 2023, enforces stringent privacy measures and accountability requirements.
-
Oman’s Personal Data Protection Law:
In effect since February 2023, this regulation emphasizes transparency and consent in data processing.
-
Qatar’s National Data Privacy Office:
Actively enforces the Personal Data Privacy Protection Law (PDPPL), focusing on consumer data protection.
-
Kuwait’s CITRA Draft Law:
Expected to become effective in 2024, it represents Kuwait’s commitment to data governance.
These regulations, coupled with sector-specific laws like Bahrain’s PDPL and the UAE’s upcoming executive regulations, underscore the region’s dedication to establishing robust privacy standards.
Understanding the Importance of Privacy-Driven Business Strategy
Consumer trust is directly linked to data privacy practices. A survey revealed that 60% of consumers have taken direct action, such as deleting apps or switching services, due to privacy concerns. Embedding privacy into business strategies is no longer optional—it is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.

Emerging Trends in Data Privacy to Watch
AI and Automation in Privacy Operations
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing how businesses manage data privacy. By automating repetitive and complex processes, AI in data privacy enhances efficiency and accuracy. Key applications include:
-
Personal Data Discovery:
AI tools can identify and classify sensitive information across databases.
-
Consent Management:
Automated systems track and manage user consents, ensuring compliance with dynamic regulatory requirements.
-
Breach Detection:
AI-powered algorithms monitor systems for anomalies, enabling rapid response to potential data breaches.
Regulatory Fluidity
As technology outpaces legislation, governments worldwide are adapting laws to address new challenges. In the GCC region, the focus is shifting toward:
- AI ethics and its implications on privacy.
- Data sovereignty and cross-border data transfer regulations.
- Sector-specific privacy mandates for industries like banking, telecom, and healthcare.
- This fluidity demands that organizations build compliance programs capable of adapting to frequent changes in the legal landscape.
The Rise of Privacy-Sensitive Consumers
Modern consumers are more aware of their data rights than ever. Research shows:
-
74% of consumers prefer brands
that prioritize the ethical use of personal information.
-
60% take proactive steps
, such as deleting apps or switching services, if privacy concerns arise
Organizations must respond to these preferences by embedding transparency and accountability into their privacy practices.
Integration of Privacy into Business Strategy
Privacy is no longer just a compliance issue—it’s a competitive differentiator. Companies are transitioning from treating privacy as a policy to viewing it as a cornerstone of customer service. This approach involves:
- Prioritizing customer education on data use and privacy rights.
- Creating seamless user experiences that align with privacy regulations.
Focus on Data Ethics
Beyond legal compliance, businesses are increasingly focusing on ethical data practices. This includes:
- Ensuring transparency in AI-driven decision-making.
- Avoiding bias in automated systems.
- Fostering trust by demonstrating accountability in data use.
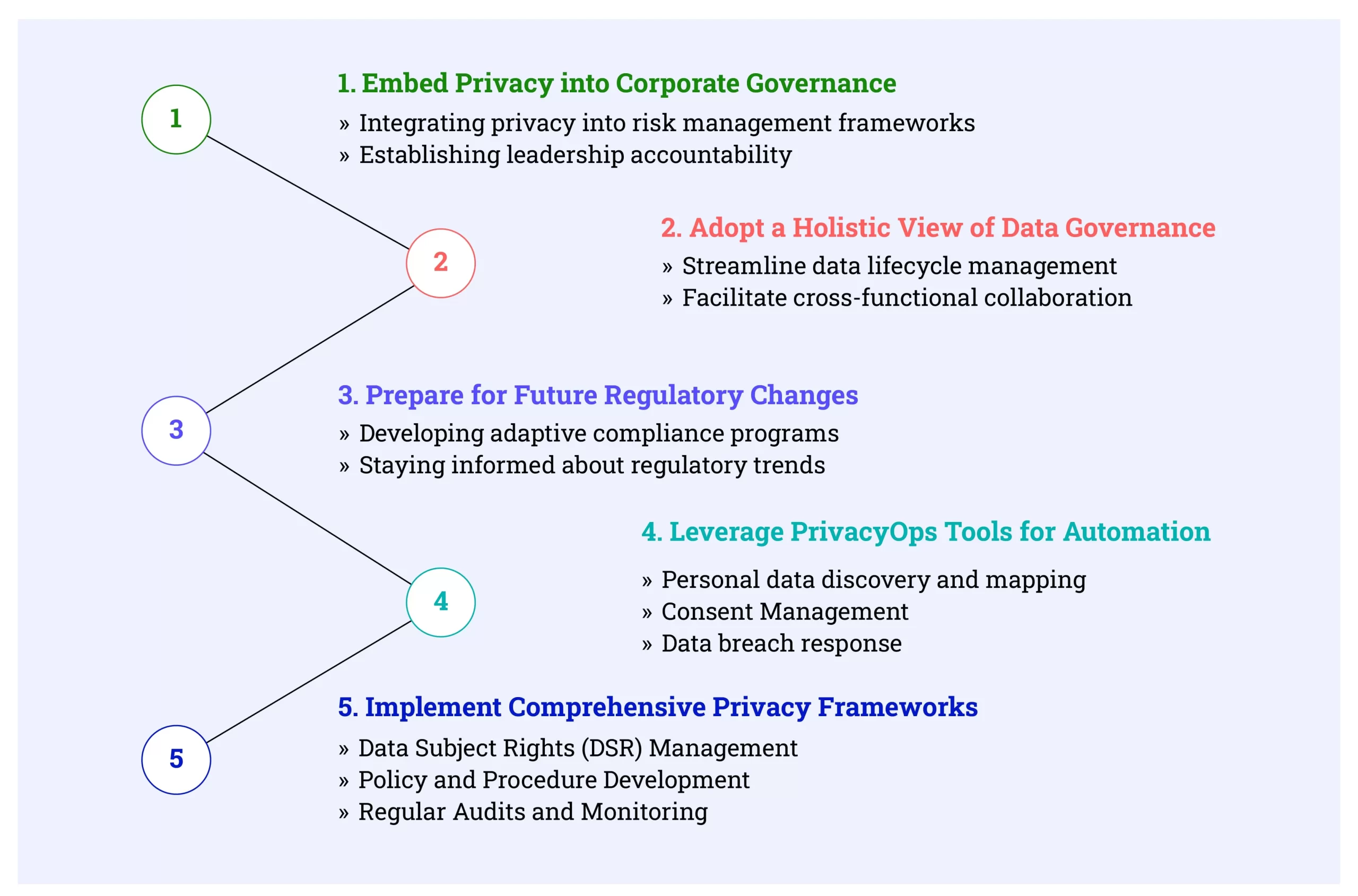
Strategies for Building an Effective Privacy Compliance Program
Here are essential strategies to design and implement an effective program:
Embed Privacy into Corporate Governance
Making privacy a priority at the executive and board levels is vital for fostering a culture of accountability. Key steps include:
-
Integrating privacy into risk management frameworks:
Treat data privacy as a critical component of overall risk governance
-
Establishing leadership accountability:
Assign privacy responsibilities to senior executives, ensuring oversight and commitment at the highest levels.
Adopt a Holistic View of Data Governance
Privacy must be part of the broader data governance framework to ensure efficiency and consistency. This approach helps organizations:
-
Streamline data lifecycle management:
Ensure every stage complies with privacy regulations from data creation to deletion.
-
Facilitate cross-functional collaboration:
Align IT, legal, and operational teams on privacy goals and responsibilities.
Prepare for Future Regulatory Changes
Privacy laws are continuously evolving, making adaptability a cornerstone of compliance programs. Strategies to future-proof include:
-
Developing adaptive compliance programs:
Design systems that can accommodate new regulations without major disruptions.
-
Staying informed about regulatory trends:
Monitor updates in GCC laws, GDPR, and other relevant frameworks.
Leverage PrivacyOps Tools for Automation
PrivacyOps tools streamline and automate critical processes, making compliance more efficient and reducing manual effort. Key use cases include:
-
Personal data discovery and mapping:
Automating the identification and classification of sensitive data across systems.
-
Consent Management:
Using tools to track user consent in compliance with regulations.
-
Data breach response:
Enabling swift and efficient responses to incidents.
Implement Comprehensive Privacy Frameworks
A scalable and adaptable framework ensures that privacy measures evolve alongside business needs. Essential components include:
-
Data Subject Rights (DSR) Management:
Simplify handling of data access, rectification, and erasure requests.
-
Policy and Procedure Development:
Establish clear data handling, storage, and processing guidelines.
-
Regular Audits and Monitoring:
Continuously evaluate compliance against evolving standards.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Privacy Compliance
Building and maintaining effective privacy compliance requires actionable strategies that address organizational, technological, and human factors. Below are practical tips to streamline privacy compliance and stay ahead of evolving regulations.
Clarify Accountability
Ensure clear lines of responsibility for privacy compliance across the organization.
- Assign an executive-level privacy leader, such as a Chief Privacy Officer (CPO), to oversee compliance efforts.
- Develop a governance structure that defines roles and accountability at every level.
Implement PrivacyOps Tools
Leverage automation to simplify and streamline privacy-related processes.
-
Data Mapping:
Automate the discovery and classification of personal data across systems.
-
Consent Management:
Use tools to track user consents dynamically, ensuring compliance with local and global regulations.
-
Breach Response:
Implement systems for rapid incident detection and resolution.
Build a Comprehensive Privacy Framework
Develop a scalable and adaptable framework to support privacy initiatives.
-
Data Discovery and Mapping:
Regularly identify where personal data resides and how it’s processed.
-
Breach Response Plans:
Create detailed response procedures to mitigate damage in case of a data breach.
-
Policy Standardization:
Establish clear and consistent data handling policies across all departments.
Foster a Privacy-Aware Culture
Educate employees on the importance of privacy and their role in compliance.
- Conduct regular training sessions tailored to different roles within the organization.
- Establish clear guidelines for secure data handling and raise awareness about potential risks, such as sharing sensitive data on social media.
Monitor and Adapt
Continuously review and improve privacy processes to ensure alignment with regulatory changes.
-
Regular Audits:
Schedule periodic privacy audits to identify gaps and implement corrective actions.
-
Risk Assessments:
Continuously evaluate data processing activities
-
Adaptability:
Update policies and practices as new regulations or technologies emerge.
How Paramount Can Help
Paramount offers an end-to-end suite of privacy services, including:
-
Gap Assessments:
Identifying compliance gaps against GCC laws.
-
Advisory and Consulting:
Developing privacy governance structures.
-
Automation and Implementation Services:
Streamlining data privacy processes.
-
Continuous Monitoring:
Conducting regular risk assessments and employee training.
Conclusion
Data privacy compliance is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity in the modern business landscape. Organizations that treat privacy as an integral part of their strategy, rather than a regulatory burden, stand to gain compliance, consumer trust, and a competitive edge. With support from experts like Paramount and cutting-edge tools, achieving comprehensive privacy compliance is a goal within reach for every business.

Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of Privacy Compliance Success
1. Saudi Telecom Company:
By automating over 100 processes, the company mitigated compliance risks and enhanced its privacy impact assessments. The result was a stronger alignment with Saudi Arabia’s PDPL.
2. GCC Bank:
Through a comprehensive personal data discovery and mapping exercise, the bank automated over 500 processes, achieving compliance with country-specific PDPL regulations.
Recent Posts

Protect your online assets from cyber threats with Paramount

Comprehensive cyber security solutions for individuals and businesses

Significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats and ensure a safer digital environment.
