Blog
Preparing for AI in Cybersecurity: A Strategic Guide for Businesses

Preparing for AI in Cybersecurity: A Strategic Guide for Businesses
With the rapid adoption of AI technologies, cybersecurity is transforming at an unprecedented pace. AI enables faster threat detection, effective mitigation of complex attacks, and improved response times. However, it also brings new risks and requires a thoughtful, strategic approach to integrate safely and effectively into security frameworks. According to a 2023 report, global cybercrime costs are projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This guide covers the essentials for businesses preparing to adopt AI in cybersecurity.
Why AI is Transforming Cybersecurity?
AI is reshaping cybersecurity by enabling enhanced threat intelligence, anomaly detection, and automation. Traditional cybersecurity defenses often struggle to keep up with sophisticated attacks. In contrast, AI’s ability to process massive amounts of data in real-time provides organizations with advanced tools to predict, detect, and respond to threats more proactively and efficiently. AI-driven systems, particularly those involving machine learning and generative AI models, support organizations in staying ahead of emerging threats.

1. Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI):
This AI category excels in tasks requiring specific rule-based algorithms, such as monitoring network activity or assessing system vulnerabilities. ANI is often embedded in systems like Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools and can efficiently handle repetitive tasks with high accuracy.
2. Generative AI:
Generative AI, like ChatGPT and DALL-E, has garnered significant attention for its creative applications, but it also holds promise for cybersecurity. It can help simulate potential attack scenarios, assist in threat modeling, and even generate natural language insights into threat landscapes. However, it also introduces risks that organizations must address.
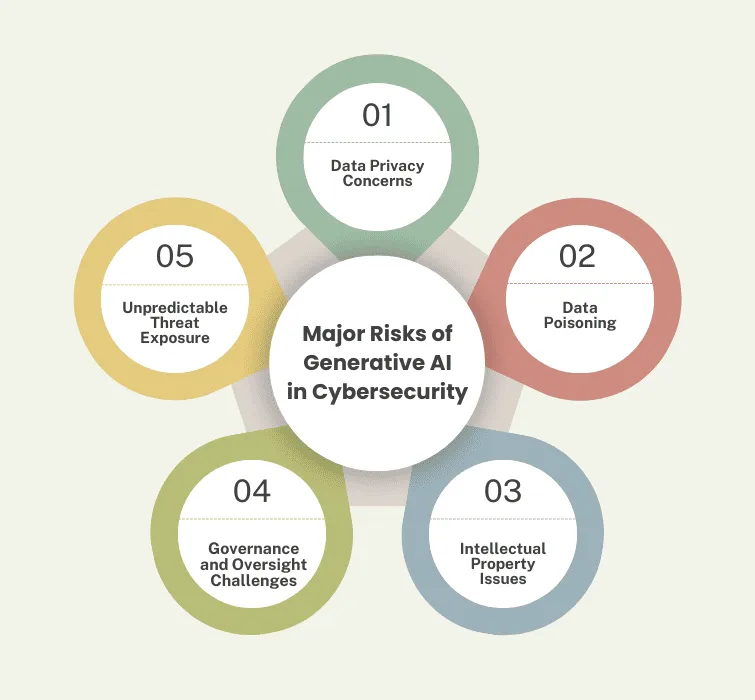
Despite its benefits, generative AI introduces several risks that could jeopardize an organization’s security.
-
Data Privacy Concerns:
Generative AI systems often require large datasets, raising concerns about the misuse or exposure of sensitive information.
-
Data Poisoning:
Cyber attackers may inject false data into training datasets, compromising the integrity of AI models.
-
Intellectual Property Issues:
Generative AI models can unintentionally leak proprietary data or be used to reproduce intellectual property without authorization.
-
Governance and Oversight Challenges:
Unlike rule-based AI, generative AI requires robust governance mechanisms to monitor its outputs and prevent unintended consequences.
-
Unpredictable Threat Exposure:
The flexibility of generative AI models can make them vulnerable to exploitation in ways that traditional AI systems are not.
Capabilities and Limitations of AI in Cybersecurity
AI in cybersecurity is highly capable but not without limitations. Knowing where AI excels and where it falls short can help organizations deploy it effectively.
Capabilities:
-
Threat Detection and Anomaly Identification:
AI excels at recognizing patterns and anomalies in large datasets, making it ideal for identifying potential threats. Machine learning models can sift through network data to detect unusual activity, potentially catching threats that traditional systems might miss. AI can reduce false positives in threat detection by up to 95%, freeing up human analysts to focus on real threats and increasing the efficiency of security operations.
-
Predictive Analysis and Threat Intelligence:
AI-powered tools can analyze historical attack data to predict potential future threats. By identifying patterns and behaviors commonly associated with attacks, AI can help organizations anticipate security risks before they escalate, allowing for preemptive measures.
-
Incident Response and Automation:
AI’s ability to automate repetitive tasks allows it to streamline incident response processes. Security teams can use AI to prioritize alerts, automate response actions, and even investigate incidents, freeing up resources for higher-level strategy and decision-making. This efficiency helps reduce the mean time to detect (MTTD) and the mean time to respond (MTTR) to incidents.
-
Fraud Detection and Prevention:
In industries like banking, AI models are crucial for detecting fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction patterns and flagging suspicious behavior. This proactive fraud prevention helps protect both customers and organizations from financial losses and reputational damage.
-
Adaptive Security Measures:
AI tools can adapt to new threats as they emerge. For example, adaptive authentication systems use AI to assess a user’s behavior and risk level, dynamically adjusting authentication requirements based on real-time data. This capability is crucial for protecting sensitive systems without sacrificing user experience.
Limitations:
-
Data Quality and Availability:
AI relies on vast amounts of high-quality data to function accurately. However, gathering and curating this data can be challenging, especially for smaller organizations with limited resources. Poor-quality or insufficient data can lead to inaccurate models, which may miss threats or generate false positives, undermining trust in AI systems.
-
Limited Generalization to Novel Threats:
While AI models are excellent at identifying known patterns, they may struggle to recognize novel threats that deviate from their training data. New, sophisticated attack techniques can bypass AI-based detection if they exploit methods the model hasn’t encountered before, highlighting the need for continuous retraining and updates.
-
Resource Intensive and Costly:
AI models require considerable computing power, data storage, and specialized expertise, making them costly to develop and maintain. Organizations must balance the benefits of AI with these resource demands, which can be prohibitive for smaller companies or those with limited cybersecurity budgets.
-
Lack of Explainability and Transparency:
Many AI algorithms, especially deep learning models, operate as “black boxes,” meaning it’s difficult to understand how they reach certain conclusions. This lack of transparency can be problematic in cybersecurity, where accountability and clear reasoning are critical. In regulated industries, this can also complicate compliance and governance.
-
Susceptibility to Data Poisoning and Adversarial Attacks:
Cybercriminals can intentionally manipulate training data in a tactic known as “data poisoning” to disrupt AI models or alter their outputs. Adversarial attacks, where slight modifications to input data trick AI models, can also undermine AI effectiveness. These risks require robust data integrity and security measures to protect AI applications.
-
Dependence on Human Oversight and Maintenance:
Despite its autonomy, AI in cybersecurity still needs human oversight to handle complex, contextual decision-making and maintain model relevance through continuous updates. Security teams must monitor AI-driven alerts and validate AI outputs, as over-reliance on AI can lead to blind spots and reduced responsiveness.
An actionable roadmap might start with mature areas for AI intervention like System Hardening, Patch Management, and Incident Monitoring. As AI technology and governance improve, organizations can expand into emerging domains such as Threat Intelligence and Hunting and Secure Architecture Design.
Webinar: Get Expert Insights on AI-Driven Cybersecurity
To dive deeper into AI’s impact on cybersecurity, businesses can benefit from webinars that explore practical applications, case studies, and expert insights. Paramount’s recent webinars, for instance, discuss advanced AI methodologies, strategies for mitigating AI risks, and best practices for integrating AI into cybersecurity frameworks. Attendees can learn from seasoned experts like Pradeep Menon and Jayesh Devadiga, who bring extensive industry experience and insights into developing secure, compliant AI-driven cybersecurity systems.
Paramount’s Role in Helping Organizations
Paramount plays a pivotal role in guiding organizations through the complexities of AI-driven cybersecurity. They offer consulting services to evaluate AI readiness, deploy secure AI tools, and maintain governance frameworks. With expertise across industries, Paramount helps businesses harness AI to bolster security operations, focusing on compliance and strategic security frameworks.
Conclusion
Integrating AI into cybersecurity is a strategic necessity for businesses facing ever-evolving threats. By understanding AI’s potential, risks, and applications, organizations can develop robust security frameworks that protect their assets and ensure data privacy. Gartner estimates that 50% of all security software products will leverage AI by 2025 to enhance detection and automation, underscoring the rapid adoption of AI in the field.
Paramount’s expertise and resources provide a solid foundation for businesses embarking on this journey, guiding them through the complexities of AI adoption and cybersecurity optimization.

Case Study Highlights: How AI Enhances Security Operations
In a recent case study, an organization faced significant delays in incident response due to manual processes. By partnering with Paramount to implement an AI-powered incident response system, the organization reduced response times and enhanced threat detection accuracy. This transformation highlights how AI can streamline security workflows, improve threat visibility, and ultimately safeguard critical data and assets.
Recent Posts
- Building a Strong Human Defense Against Cyber Threats in the Middle East
- How to Choose the Right Cybersecurity Consulting Partner in the Middle East
- Best Practices for Implementing Robust OT Security
- Securing Digital Identities: Why Identity is at the Core of Cybersecurity in the Middle East
- Value-Driven Cybersecurity

Protect your online assets from cyber threats with Paramount

Comprehensive cyber security solutions for individuals and businesses

Significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats and ensure a safer digital environment.
