Blog
Securing Digital Identities: Why Identity is at the Core of Cybersecurity in the Middle East

Securing Digital Identities: Why Identity is at the Core of Cybersecurity in the Middle East
Digital identities are the keys to accessing critical resources and data in today’s connected world. As organizations shift more of their operations online, they face increasing cyber threats targeting their identity systems. Understanding the importance of protecting digital identities—and implementing the right strategies to manage them—has never been more crucial for businesses in the region.
This blog explores why identity is at the core of cybersecurity and how organizations can better safeguard their systems against identity-based threats.
The Importance of Identity in Cybersecurity for Middle Eastern Organizations
A rapidly expanding digital ecosystem in the Middle East has seen a region-leading 24% increase in cyberattacks between 2021 and 2023, with many attacks exploiting identity and access vulnerabilities. This makes digital identity protection in GCC critical to a cybersecurity strategy. Digital transformation across industries—especially in banking, healthcare, and government—has introduced increased reliance on cloud services, digital identities, and hybrid working environments, creating an ever-growing attack surface.
Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) is not just a convenience; it is essential. Organizations must ensure the right people have the appropriate access to critical resources at the right times. Mismanagement of digital identities can lead to risks like entitlement creep, orphaned accounts, and compliance failures, which are particularly costly in this region.
Why Identity-Centric Attacks Are on the Rise
Identity is now the most exploited attack vector globally, and the Middle East is no exception. Several factors drive this trend:
- Expanding Attack Surfaces: Integrating Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications and legacy systems increases vulnerability.
- Identity Silos: Disparate identity data creates inconsistencies and blind spots, making it easier for attackers to exploit gaps.
- Sophisticated Threats: Cybercriminals employ social engineering and identity-based tactics, often targeting poorly managed credentials and access processes.
Recent data breaches, including some targeting the GCC region, underscore how poorly managed identity and access controls can lead to devastating consequences.
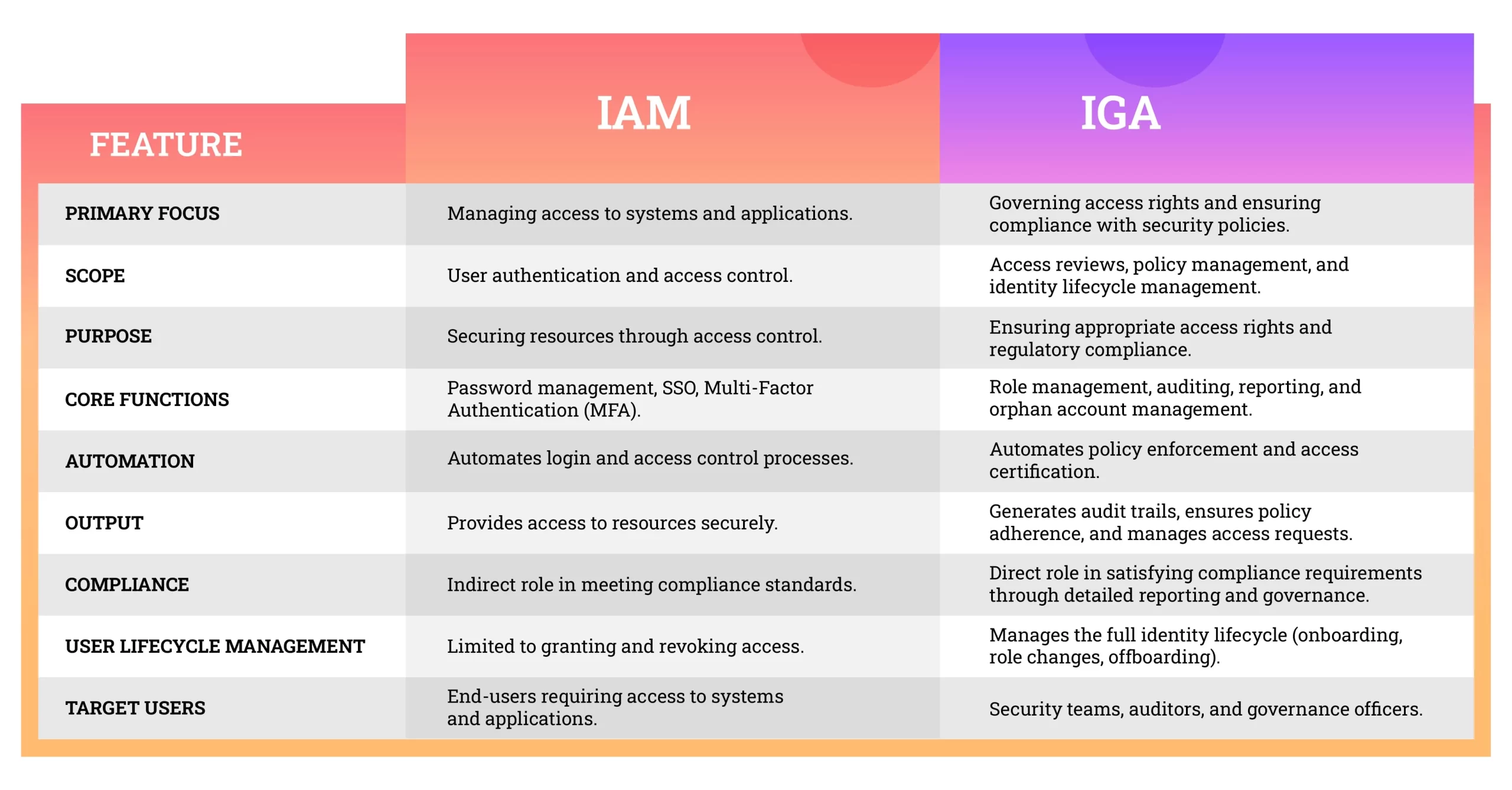
IAM vs. IGA: What’s the Difference?
Identity Access Management (IAM) and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) are complementary components of identity-centric security, but they serve different purposes. Understanding their distinctions is critical for building a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
IAM: Identity Access Management
1. Definition: IAM solutions focus on managing and controlling access to digital
resources by verifying user identities and determining what they can access.
2. Primary Objective: Ensures secure and streamlined access to systems and data.
3. Key Functions: Authentication, authorization, and single sign-on (SSO).
IGA: Identity Governance and Administration
1. Definition: IGA emphasizes the governance of identities, ensuring that users have appropriate access and that this access is regularly reviewed and adjusted.
2. Primary Objective: Align identity management processes with compliance, security, and operational requirements.
3. Key Functions: Access reviews, policy enforcement, compliance reporting, and lifecycle management.
The Importance of Implementing IGA for Middle Eastern Organizations
IGA solutions play a vital role in addressing the unique cybersecurity challenges in the Middle East:
- Compliance: Regulatory frameworks in the GCC often mandate stringent identity and access control measures. IGA simplifies audit and reporting requirements, ensuring local and international standards compliance.
- Risk Mitigation: Automated IGA systems eliminate orphan accounts and unauthorized access, reducing the risk of breaches.
- Operational Efficiency: IGA enhances resource allocation and reduces manual workloads by automating lifecycle management.
Best Practices and Common Mistakes in IGA Implementation
Implementing Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) is a critical step for organizations in managing digital identities effectively. However, the success of IGA initiatives often hinges on following best practices and avoiding common mistakes.
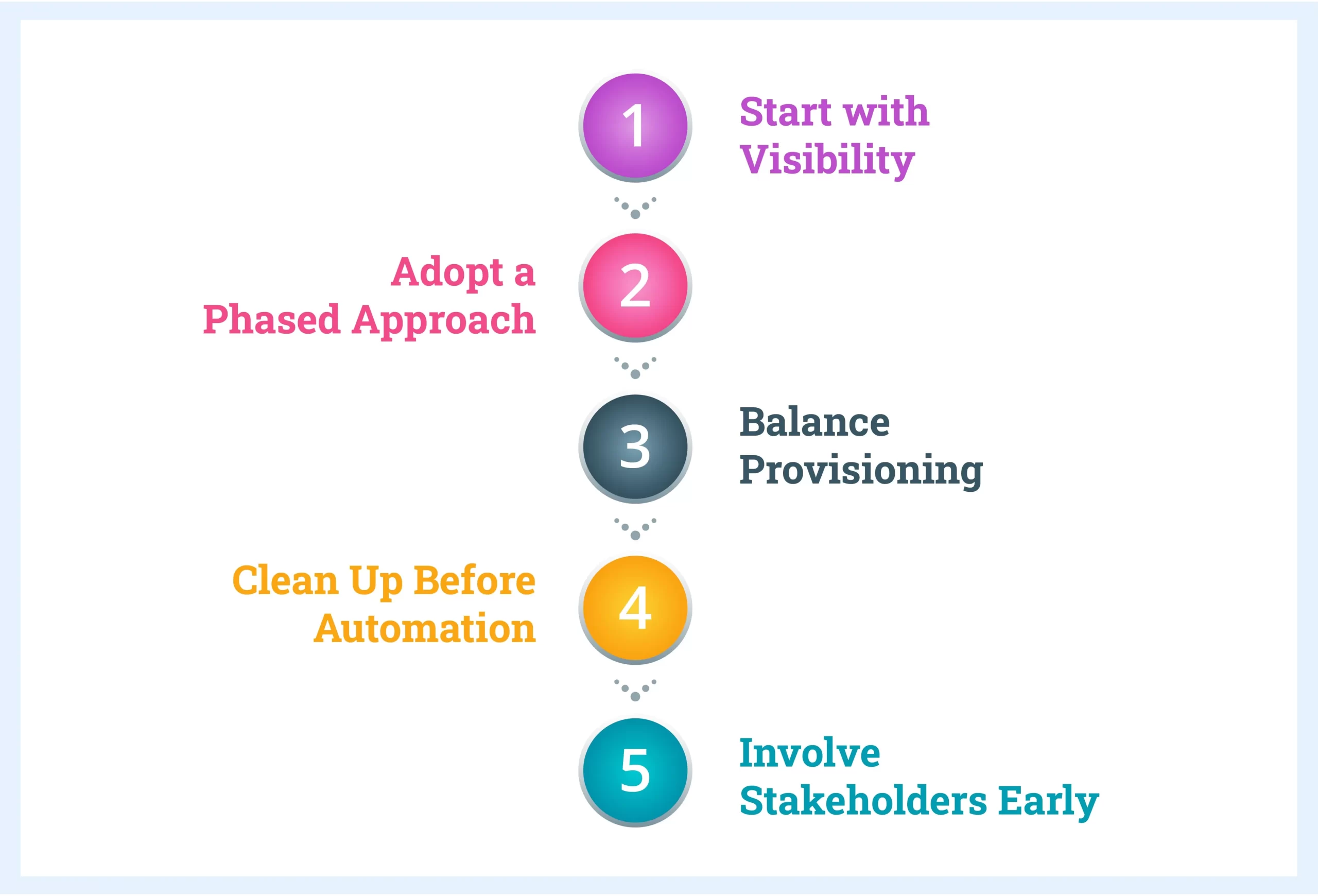
Best Practices in IGA Implementation
Start with Visibility
1. What to Do: Begin by mapping out all existing accounts, roles, and access permissions. Identify orphaned accounts, dormant accounts, and redundant entitlements.
2. Why: Establishing visibility helps identify potential risks and sets the groundwork for a structured IGA framework.
Adopt a Phased Approach
1. What to Do: Roll out IGA in stages, starting with essential governance components before tackling full automation.
2. Why: This allows for adjustments, minimizes disruptions, and ensures each phase is aligned with organizational goals.
Balance Provisioning
1. What to Do: Use both direct and indirect fulfillment for provisioning to avoid overcomplicating processes initially.
2. Why: End-to-end automation can be resource-intensive. Balancing manual and automated processes ensures smoother implementation.
Clean Up Before Automation
1. What to Do: Remove unnecessary and duplicate accounts and streamline permissions before introducing automated tools.
2. Why: Automating a poorly managed system will perpetuate inefficiencies and risks.
Involve Stakeholders Early
1. What to Do: Engage IT, compliance, HR, and other relevant teams from the outset.
2. Why: Cross-department collaboration ensures the IGA solution aligns with business needs and regulatory requirements.
Common Mistakes in IGA Implementation
Skipping the Clean-Up Phase
- Mistake: Ignoring the removal of redundant or dormant accounts before implementing IGA.
- Consequence: This creates inefficiencies, risks, and compliance issues from the start.
Excessive Focus on Automation
- Mistake: Attempting to automate all IGA processes from the outset without proper groundwork.
- Consequence: Leads to complex, unmanageable systems prone to errors.
Underestimating Governance
- Mistake: Treating IGA as just an IT project rather than a governance initiative.
- Consequence: Results in misaligned policies and non-compliance with regulatory standards.
Neglecting Stakeholder Buy-In
- Mistake: Not involving key departments like HR and compliance in the IGA planning phase.
- Consequence: Leads to poor adoption and ineffective identity processes.
Overlooking User Education
- Mistake: Failing to train users on IGA tools and processes.
- Consequence: Reduces the efficiency and accuracy of identity management.
How Paramount Assure Can Help with Identity Governance and Administration
Paramount Assure specializes in tailored IGA solutions for Middle Eastern organizations, combining local expertise with global best practices. Their services include:
- Advanced Dashboards and Analytics: Providing actionable insights into identity lifecycle management.
- Policy and Compliance Management: Ensuring seamless compliance with GCC regulations.
- Operational Optimization: Improve efficiency by automating provisioning, certification, and role management.
Steps to Implementing an Effective IGA Program
Establishing a robust Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) program is a structured process that enhances security, compliance, and operational efficiency. Organizations face 25-30% annual growth in access permissions, which increases risks of unauthorized access. Below is a step-by-step guide to help organizations implement an effective IGA framework.
Identify High-Risk Areas
1. What to Do:
Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities in identity management processes.
2. How:
Audit existing accounts, roles, and access permissions.
Highlight orphaned accounts, entitlement creep, and unauthorized access.
3. Why:
Knowing where the risks lie helps prioritize efforts and resources.
Define Clear Objectives
1. What to Do:
Establish clear goals for the IGA program.
2. How:
Align objectives with organizational priorities, such as regulatory compliance or operational efficiency. 65% of Middle Eastern organizations identified regulatory compliance as a primary driver for adopting identity governance solutions.
Define key metrics to measure success (e.g., reduced access review times or compliance rates).
3. Why:
Clear goals ensure the program addresses business needs and delivers measurable value.
Choose the Right IGA Solution
1. What to Do:
Select an IGA solution tailored to your organization’s size, industry, and regulatory requirements.
2. How:
Evaluate vendors based on features like lifecycle management, reporting, and compliance tools.
Ensure scalability to accommodate future growth.
3. Why:
The right solution provides the foundation for effective governance and automation.
Build a Cross-Functional Team
1. What to Do:
Assemble a team from IT, HR, compliance, and other relevant departments.
2. How:
Define roles and responsibilities for each stakeholder.
Foster collaboration between teams to align technical and governance needs.
3. Why:
A multidisciplinary approach ensures the program is holistic and well-integrated.
Establish Governance Policies
1. What to Do:
Create policies to define access rights, role hierarchies, and compliance requirements.
2. How:
Develop Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) frameworks.
Set rules for access requests, provisioning, and reviews.
3. Why:
Governance policies are the backbone of an IGA program, providing clarity and consistency.
Begin with a Phased Rollout
1. What to Do:
Implement the IGA program incrementally.
2. How:
Start with foundational elements like visibility and access reviews.
Gradually introduce automation for provisioning and certification processes.
3. Why:
A phased approach reduces disruptions and allows for iterative improvements.
Automate Identity Lifecycle Management
1. What to Do:
Use the IGA system to manage the entire lifecycle of digital identities.
2. How:
Automate onboarding, role changes, and offboarding processes.
Set up alerts for entitlement changes or suspicious activities.
3. Why:
Automation minimizes manual errors and improves efficiency.
Integrate Advanced Analytics
1. What to Do:
Leverage analytics to gain insights into identity usage and compliance trends.
2. How:
Use dashboards to monitor access requests, role assignments, and policy adherence.
Identify anomalies, such as dormant accounts or unusual login patterns.
3. Why:
Data-driven decisions improve the program’s effectiveness and adaptability.
Test and Refine the Program
1. What to Do:
Regularly test the IGA system to identify gaps and inefficiencies.
2. How:
Conduct simulated audits to evaluate compliance and security posture.
Collect feedback from users and stakeholders for continuous improvement.
3. Why:
Testing ensures the program evolves to meet changing business needs and threats.
Establish Continuous Monitoring and Reviews
1. What to Do:
Make monitoring and periodic access reviews a standard practice.
2. How:
Schedule automated access certification processes.
Use real-time alerts to address security incidents promptly.
3. Why:
Continuous oversight helps maintain compliance and prevents entitlement creep.
Conclusion
Identity is the backbone of cybersecurityin the Middle East, especially as organizations continue to adopt advanced digital solutions. By prioritizing IGA and adopting best practices, businesses can reduce risks, enhance compliance, and improve operational efficiency. Partnering with experts like Paramount Assure ensures that these goals are achieved effectively.

Case Study: IGA Implementation for a Leading EMEA Bank
A major bank in the GCC with over 150,000 users faced compliance failures and inefficient manual processes for access reviews. After implementing an IGA solution:
- Results: Reduced access review time from 84 days to just three days.
- Improvements: Cleaned up 30,000 orphan accounts and 15,000 dormant accounts.
- Outcomes: Passed compliance requirements and achieved significant cost savings.
Recent Posts
- Best Practices for Implementing Robust OT Security
- Effective Data Security Strategies: A Comprehensive Guide for Middle Eastern Businesses
- How to Choose the Right Cybersecurity Consulting Partner in the Middle East
- Cloud Security Best Practices
- Why is choosing the Right Security Operations Center Necessary?

Protect your online assets from cyber threats with Paramount

Comprehensive cyber security solutions for individuals and businesses

Significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats and ensure a safer digital environment.
